Back pain
If you have back pain, you are not alone; about 80 percent of adults experience some form of back pain in their lifetimes. Back pain is the most common cause of job-related disability and a leading contributor to missed workdays. The treatment of low back pain (LBP), in particular, runs at least $50 billion in US healthcare costs each year. If you're among that group, Sussex Pain Relief Center in Georgetown and Lewes, Delaware, wants you to stop suffering needlessly. Manonmani Antony, MD, DABA, DABIPP, and her team offer comprehensive interventional pain management care for chronic back pain, with the goal of taking your life back as soon as possible. Call the office nearest you or use the online booking button now.
Back pain FAQ
What are the types of back pain?
Low back pain is one of the most common types of back pain. Most low back pain is acute, or short term, and lasts a few days to a few weeks. It tends to resolve on its own with self-care and there is no residual loss of function.
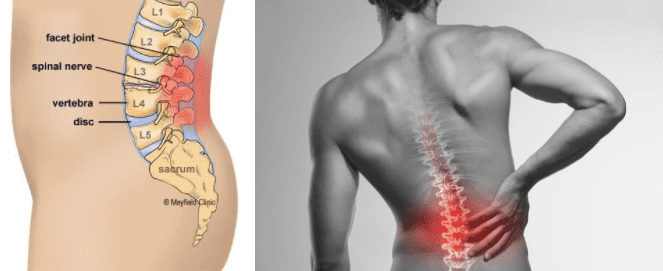
Chronic back pain is defined as pain that persists for 3 months or longer, even after an initial injury or underlying cause of acute low back pain has been treated. About 20% of people affected by acute low back pain develop chronic low back pain with persistent symptoms at one year.
What are the causes of back pain?
The back is a complex structure that is composed of muscles, tendons, ligaments, bones, and intervertebral discs. Problems in any of the structures that make up the lumbar spine can result in pain. Back pain can be caused by any of the following:
Injury or trauma
A motor vehicle injury, sports injury, fall, or strenuous activity can strain or tear muscles and ligaments.
Bulging or herniated disc
Between each vertebra in the spine is an intervertebral disc. The gel-like center of a spinal disc can bulge or rupture through a weak area in the wall and compress nerves.
Pinched nerve or sciatica
A herniated or bulging disc may create a sharp, shooting pain that travels from the back, through the buttock and down the back of the leg.
Arthritis or facet joint syndrome
Osteoarthritis is a common condition that can affect multiple joints of the body, including the facet joints of the spine. Facet joints are located between each vertebra of the back and along the bony ridge of the lumbar spine. Arthritis of facet joints has been shown to be a source of pain in the back and referred pain in the buttocks and back of the thighs.
Degenerative disc disease
As discs naturally age they dry out and shrink; bone spurs can form.
Spinal stenosis
Narrowing of the spinal canals in the spine can compress the spinal cord and nerves causing pain, numbness, or weakness in the legs. Symptoms are typically gradual in onset and improve with bending forward.
Spinal deformity
Scoliosis and kyphosis are two types of abnormal spinal curvatures that can result in pain.
Myofascial pain syndrome
Myofascial pain is unique in that it's associated with trigger points—areas of tenderness and stiffness within the muscle tissue that reduce your range of motion.
Spinal fracture
A compression fracture is typically caused by a loss of bone mass (osteoporosis) that occurs as part of aging. A fall, cough, or lifting of a heavy object may cause a fracture of the backbones causing back pain, lost height, and a hunched-forward posture.
Sacroiliac joint pain
This pain is caused by damage or injury to the joint between the spine and hip.
Post-surgical pain
Pain after lumbar spine surgery. As the back continues to heal, patients usually start to feel better and find they can take on more activities. The worst pain is generally over by 4 weeks after surgery. Pain is likely to continue to decrease gradually, but some patients continue to have pain 3 to 6 months after surgery.
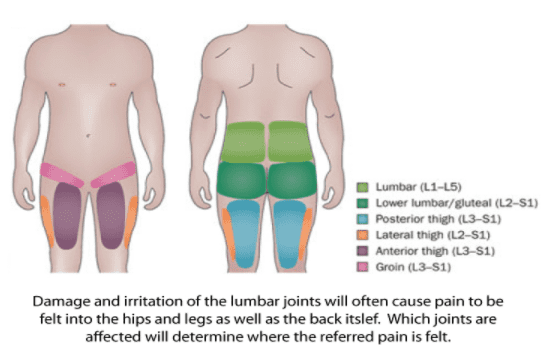
What is the difference between acute and chronic back pain?
Acute back pain is short-term pain, usually triggered by an injury, that typically goes away within a week. Chronic back pain goes on for weeks, months, even years.
Some cases of back pain, like pain after an auto accident or workers' compensation (on-the-job) injury, start out as acute pain. The pain never abates as expected, however, and you're left with chronic back pain.
Other causes of chronic back pain develop slowly, such as arthritis, that can be common due to spinal joint damage.
Whether you have acute or chronic back pain, it's best to reach out for pain relief now. With all of the advanced new procedures available at Sussex Pain Relief Center, there's no reason to hurt.
What happens during my first appointment for back pain?
The Sussex Pain Relief Center team performs an evaluation, including a physical exam and a medical history. During this time, you discuss your pain and your history of pain treatments.
A careful evaluation will help determine the type and cause of your back problem and the best treatment options. A diagnostic evaluation includes a thorough medical history, targeted physical exam, and review of imaging scans (e.g., X-ray, CT, MRI).
What back pain treatments are available at Sussex Pain Relief Center?
Your spine is just as unique as you are, and that's why Sussex Pain Relief Center customizes your back pain relief. There are dozens of possible treatments for back pain, with some common approaches including:
Lumbar epidural injections/transforaminal epidural steroid injection
The steroid injections can reduce inflammation and can be effective when delivered directly into the painful area, the epidural space of the spine.
Lumbar facet joint injections
The steroid injections can reduce inflammation and can be effective when delivered directly into the painful area, facet Joints.
Diagnostic medial branch nerve blocks
The medial branch nerve block is designed to interrupt the pain signal being carried by the medial branch nerves supplying a specific facet joint. This is performed twice using a local anesthetic to locate the target nerve.
Radiofrequency ablation of medial branch nerves
Once the RFA heat lesion is created, the pain-transmitting ability of the nerve fibers is lost and pain signals from the facet joint do not reach the brain. The effects of RFA may last for a few months to years, after which the nerve usually regenerates, and the pain may or may not return. This procedure can be repeated after six months.
Trigger point injections
A small needle is inserted into the patient's trigger point.
Sacroiliac joint injection
with steroids is done to provide relief of the pain associated with sacroiliac joint dysfunction.
Spinal cord stimulation (SCS)
Spinal cord stimulation therapy masks pain signals before they reach the brain. A small device, similar to a pacemaker, delivers electrical pulses to the spinal cord.
Lumbar discogram
needles are inserted into the disc and filled with contrast. A CT scan identifies leakage from the discs to identify any spinal disc herniations. This is done for confirmation of a suspected disc as the source of pain, and surgical intervention is being considered.
Adhesiolysis
Percutaneous Adhesiolysis is a pain treatment that has the ability to reduce scar tissue along the spinal cord.
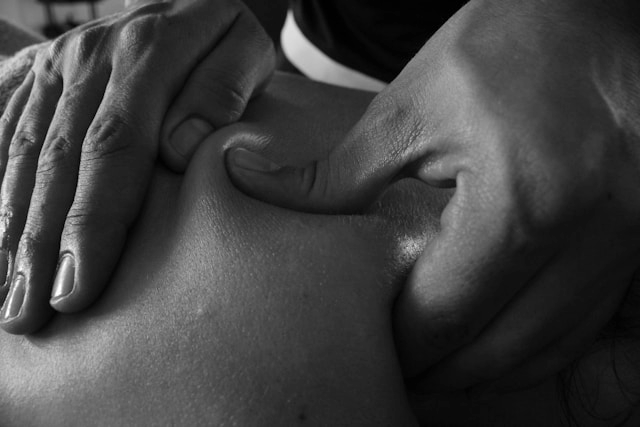
Massage therapy
Therapeutic massage may relieve pain by way of several mechanisms, including relaxing painful muscles, tendons, and joints; relieving stress and anxiety; and possibly helping to "close the pain gate" by stimulating nerve fibers and impeding pain messages to and from the brain.

In most cases, the Sussex Pain Relief Center team starts with the most conservative approach possible, such as epidural injections. If you don't get adequate relief from the most conservative measures, you might move on to other, minimally invasive procedures such as radiofrequency ablation or spinal cord stimulation.

Make your first move toward living without pain by calling Sussex Pain Relief Center or booking online now.